USBL Acoustic Positioning
USBL is a system that uses acoustic sound waves to determine position underwater. A USBL set up consists of
USBL stands for Ultra-short Baseline. It is an old, loosely defined phrase referring to an acoustic positioning system with multiple hydrophones in a single unit.
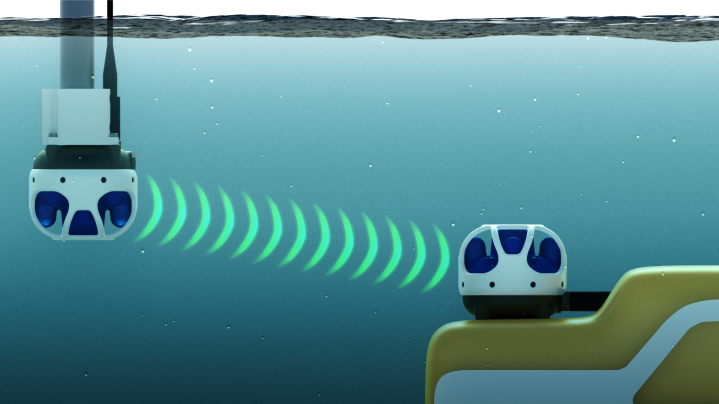
Typical USBL positioning set up
A typical USBL set up will have a USBL transceiver mounted on a pole attached to the side of a ship and another USBL transceiver mounted on a vehicle underwater, as shown above. The USBL system mounted on the pole is known as the surface unit and the USBL system underwater is known as the subsea unit.
The way a USBL system works is that
This process of transmitting and receiving acoustic sound wave signals between the USBLs alternates back and forth continuously between the two units, allowing each unit to determine the position of the other. Subsonus is able to perform acoustic positioning updates in this way at up to 10 times per second which is limited by the speed of sound through water.
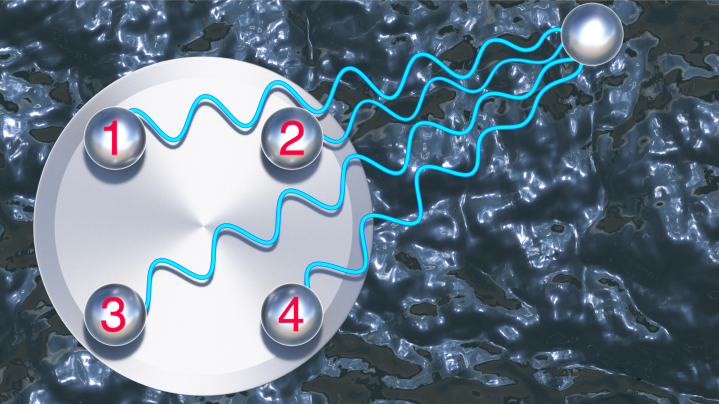
USBL hydrophones receiving acoustic sound waves shows 4 receive hydrophones which is typical of current USBL systems, however Subsonus actually uses 8 hydrophones which allows it to more accurately determine the direction and range of the acoustic signal.
Subsonus is the first low cost USBL system on the market to feature acoustic heading. Acoustic heading works by determining the angular offset between the surface and the subsea unit. This angular offset can then be subtracted from the surface unit's known accurate heading to provide accurate heading for the subsea unit.